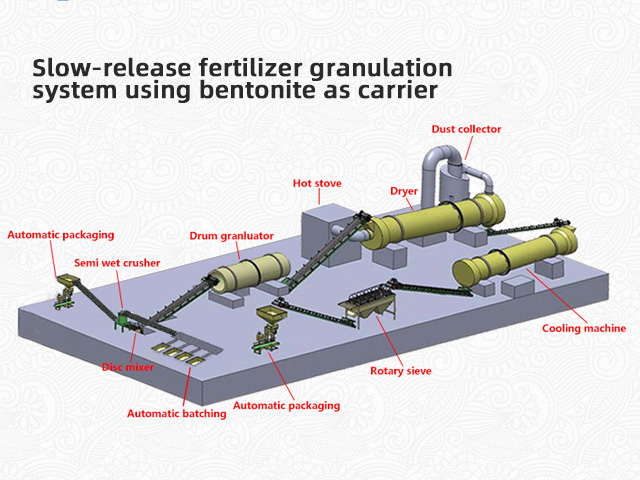
Bentonite slow-release fertilizer process equipment mainly includes the following parts:
1. Crusher: used to crush bentonite, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, urea and other raw materials into powder to facilitate subsequent processing.
2. Mixer: used to evenly mix the crushed bentonite with other ingredients.
3. Granulator: used to make the ground materials into granules for subsequent packaging and use.
4. Drying equipment: used to dry the produced particles, remove moisture and improve their stability.
5. Cooling equipment: used to cool the dried particles to prevent them from changing during packaging and use.
6. Packaging equipment: used to package the cooled particles to protect their quality and safe use.
These equipment can be combined and adjusted according to the process flow, and the specific process flow and equipment configuration can be determined according to actual production needs.
Material: “Advantages of Bentonite as Fertilizer Carrier”
In order to improve the effective utilization of fertilizers, there are a variety of slow-release fertilizers using bentonite as a carrier on the market. These slow-release fertilizers perform very well in delaying the fertilizer release process. Take bentonite nitrogen and phosphorus slow-release fertilizer as an example. Bentonite carrier nitrogen and phosphorus slow-release fertilizer was prepared by mixing bentonite, monoammonium phosphate (MAP), urea-formaldehyde resin and magnesium carbonate. The effects of bentonite type, soil-to-fertilizer ratio, urea-formaldehyde resin and magnesium salt dosage on total nitrogen and P2O5 in the slow-release fertilizer were studied. The influence law of cumulative dissolution rate was studied, and a pot experiment was conducted using red tomatoes. The research results show that the slow-release effect of sodium bentonite is better than that of calcium bentonite. The cumulative nitrogen release rate of slow-release fertilizer decreases with the increase of soil-fertilizer ratio or urea-formaldehyde resin dosage, and the optimal process conditions for its slow-release effect are: : The carrier is sodium bentonite, the soil to fertilizer ratio is 8:2, the magnesium carbonate dosage is 9%, and the urea-formaldehyde resin dosage is 20%. In addition, the application of bentonite-based slow-release fertilizer has obvious advantages over the application of monoammonium phosphate (MAP) in terms of plant height and plant leaf number. The yield of red tomatoes is increased by 33.9%, and the yield fluctuation value is smaller.
Post time: Dec-09-2023